BIOBANQUE SUISSE


Nous n'appartenons à aucun groupe financier et n'avons aucuns actionnaires à rétribuer.
C'est pourquoi nous pratiquons des formules de prix parmi les plus basses du marché et les plus populaires.
Le sang du cordon ombilical est une source précieuse de cellules souches qui peuvent être utilisées dans le
traitement de diverses pathologies, comme la leucémie et d'autres troubles sanguins. Ces cellules souches,
prélevées à la naissance à partir du cordon ombilical, offrent des options thérapeutiques potentielles pour
l'enfant et, dans certains cas, pour les membres de la famille compatibles.
Nous avons toujours établi les normes les plus élevées dans notre domaine en misant sur l’innovation scientifique, un service client de qualité et une transparence absolue. Cela nous permet de proposer une biobanque de cellules souches en Suisse de premier plan, offrant des solutions plus personnalisées et plus humaines.
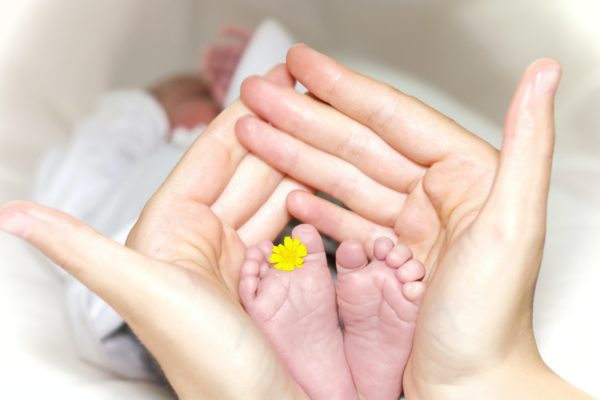

Sang de cordon ombilical
Préserver les cellules souches hématopoïétiques du sang de cordon de votre bébé, capables de produire toutes les cellules du sang et du système immunitaire. Elles ont permis de traiter plus de 80 maladies et sont utilisées dans de nombreux essais cliniques.
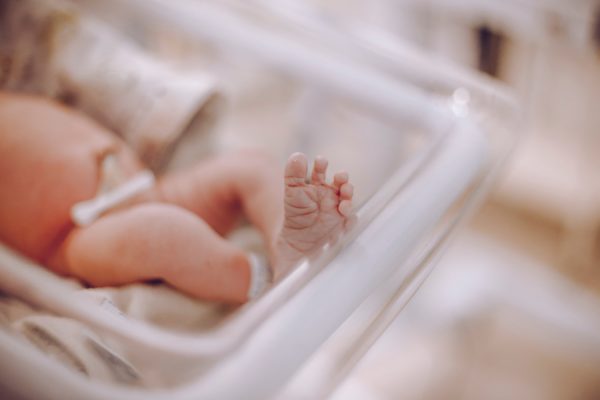

Tissu du cordon ombilical
Préserver le tissu de cordon qui est une source de cellules souches mésenchymateuses (CSM) capables de régénérer os, cartilage et muscle. Utilisées en médecine régénérative, elles sont étudiées dans plus de 1000 essais cliniques pour traiter des maladies comme la paralysie cérébrale, l’arthrite et le diabète de type I.
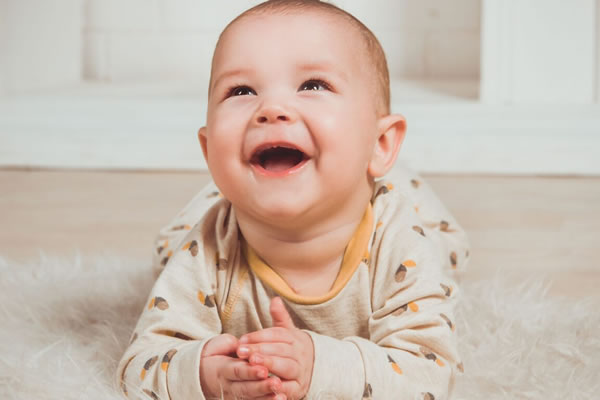

Tissu placentaire
Préserver les cellules souches placentaires, prometteuses en médecine régénérative, utilisées pour traiter des maladies comme la sclérose en plaques et les troubles neurologiques. Leur utilisation se développe, avec plus de 23 000 essais cliniques et 40 thérapies autorisées.
Notre biobanque bénéficie d’une reconnaissance internationale et est considérée comme l’un des centres de cryoconservation et de stockage biologique parmi les plus sûrs et les mieux côtés au monde. En effet, nous collaborons régulièrement avec plus de 24 pays, dont voici quelques exemples:
| Afrique du Sud | * France | Luxembourg | |||
| Allemagne | Hollande | Monaco | |||
| Autriche | Hong Kong | Pakistan | |||
| Bahrain | Inde | Pologne | |||
| Belgique | Israel | Portugal | |||
| Emirats Arabes | Italie | Roumanie | |||
| Espagne | Kenya | Slovaquie | |||
| Etats-Unis | Lettonie | Ukraine | |||
| Brésil |
* sur dérogation des autorités compétentes françaises (pourquoi ?)
CORDSAVINGS SA
Route de l’Ile-au-Bois 1A
1870 Monthey (Suisse)
Lundi – vendredi : 08.00 / 17.00
Garde pour les naissances
et les urgences 7/7 - 08.00 / 18.00

